Each headset has its own connector and pinout. These pins and connectors play a crucial role in the operation of the headphones. We will provide you with information about all types of connectors, their characteristics and pin-outs.
By the time you finish reading this article, you should be familiar with the concept of a headphone jack and the following terms:
- Lightning Jack audio jack
- Micro jack 2.5
- 3.5 mm mini-jack
- 6.3 mm jack
- USB audio jack
- Type-C
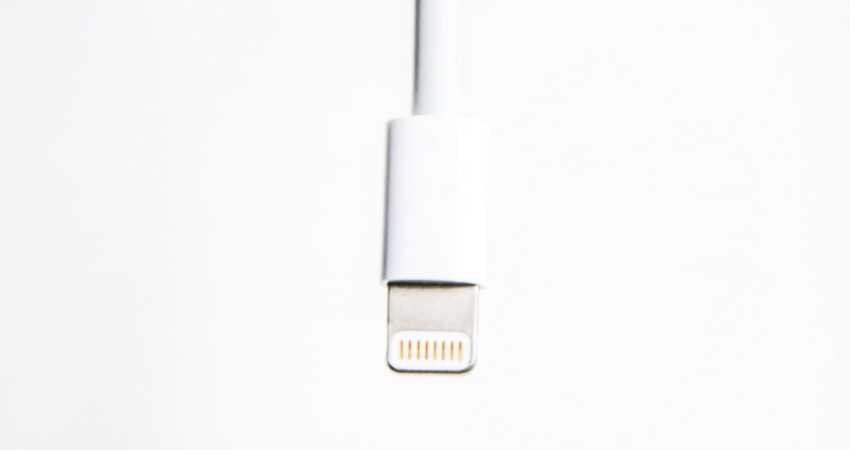

Audio Lightning Jack
The Lightning Jack has the distinction of producing output sound without reducing it. The connector or Lightning Jack produces and transmits a full sound compared to the 3.5 mm Jack, which compresses the output sound and can only transmit a 16-bit quality to the listener.
Headphones with a Lightning headphone jack have many advantages over other jacks or connectors. Here are some advantages:
- The Lightning Jack produces perfect sound reproduction without any distortion or compression of the built-in DAC
- By using the Lightning Jack, you can provide electrical power to your headphone device directly from the source
- Increased probability of digital value exchange between the headphone device and the signal source
- You can add other features to your accessories, such as digital inputs and fitness sensors
The audio jack pinout of the Lightning cable is as follows:
- Pin GND Ground
- Pin L0p Lane 0+
- L0n Lane 0-
- ID0 Identification / Control 0
- PWR Power
- L1n Lane 1 negative
- L1p Lane 1+ positive
- ID1 Identification / control 1

2.5 mm Micro-jack
Micro Jack is another name for the headphone jack. It is almost no different from the mini-jack, except for its size (2.5 mm). Previously, it was used in mobile devices, but the standard did not hold, and manufacturers decided to use in their devices a 3.5 mm plug.
If you’re looking for a very small plug, the 2.5mm jack is the smallest headphone plug. It is called a 2.5 micro jack because the diameter of the plug is 2.5 mm. The micro jack is usually used in the cables of smartphones and players. This micro-jack is only used for audio transmission, and it is difficult to find nowadays because manufacturers have started to use the mini-jack.
Many people use headphones, but only a few are aware of the properties of the plug. This usually causes them a problem. For example, if you insert the TS plug into the TRRS connector, while TRRS stands for “Tip, Ring, Ring, Sleeve.” There is a very high risk of damaging the output of your equipment while, on the other hand, when you connect a TRRS plug to a TS connector, there is no problem. This is why a basic knowledge of connectors and jacks is essential.
Wiring a headset with a TRRS 2.5 cable (OMTP standard – national standard) looks like this:
- The first channel is left
- The second channel is right
- The third channel is for the microphone connection
- The fourth channel is the ground.
A TRRS 2.5 cable (CTIA standard – American standard):
- The first channel is left
- The second channel is right
- The fourth channel is the ground
- The third channel is for the microphone connection
A TRS 2.5 cable for a standard headset:
- The first channel is left
- The second channel is right
- The fourth channel is the ground.
A 2.5 TRS cable for standard headphones:
- The first channel is the microphone
- The second channel is the audio output
- The fourth channel is the ground
Headphones with 2.5 mm Micro-jack

3.5 mm Mini-jack
The 3.5 mm Mini-jack is a very common type of connector and is used in almost all types of devices, including Apple products. This is the same plug that is now being replaced by USB Type-C and has already been replaced by Apple manufacturers. Repairing plugs of any diameter is very easy, but the Lightning or type-c plug is an exception.
Headphone jacks of the same size can also differ in the number of wires. For example, the 3.5mm plug can have 3 or 4 wires. In the first case, a mono sound is transmitted; in the second, we have a full stereo sound. In most cases, we find headphones with two-channel sound (stereo sound). If there is a microphone, it is already a headset, which means that there will be an extra pin on the connector.
The pins of the plug depend on the type of manufacturer. Here are a few characteristics about the 3.5 mm mini-jack.
- The TS cable is used to connect a microphone; having two signal conductors (positive and negative)
- The TRS cable is the most common type, suitable for all kinds of accessories. It has 3 pins, left, right and ground.
- The TRRS is older and was designed for the older Nokias. It has four pins. The first is left, the second is right, the third is the microphone, and the fourth is ground.
- There is another form of TRRS in which the first is left, the second is right, the third is the ground, and the fourth is a microphone. It is particularly designed for HTC, iPhone, Samsung, and Sony.
Headphones with 3.5 mm Mini-jack
- Beyerdynamic MMX 300 (2nd Gen)
- Microsoft Surface Headphones
- Philips SHP-6000
- Sony WH-1000XM2
- Meze 99 Neo
- Marshall Monitor II ANC
- Sennheiser HD 660 S (balanced 6.3 mm cable and unbalanced 3.5 mm cable with a 6.3 mm to 3.5 mm adapter)
- Beyerdynamic Lagoon ANC Traveler with aptX Low-Latency

6.3 mm (6.35 mm) Headphone Jack
The 6.3 mm headphone jack is a fairly old standard, which is used more in professional audio equipment. In the past, DVD players were equipped with this jack. Today, the standard headphone jack is used in musical instruments: electric guitars, etc.
Nowadays, the 6.3 mm headphone jack is very rare and rarely used. You can only see the 6.3 jack in professional music equipment, older microphone models, and metal detectors.
The headphone jack can be divided into two types depending on the number of pins. Two-pin and three-pin. Each of them has a different pinout.
For the two-pin:
- The first contact is a microphone
- The second is the ground
For the three pins:
- The first is left
- The second is ground or common
- The third is ground.
Headphones with 6.3 mm headphone jack
- Philips SHP-6000 (with 3.5 to 6.3 mm adapter)
- Meze 99 Neo (via 3.5 to 6.3 adapter)
- Sennheiser HD560S
- Meze 99 Classics (via adapter)
- MEE Audio Pinnacle P1

Connection via USB
Previously, USB was found only on computers, but today such ports are located on the cheapest LCD TVs, most music stations, some tablets. And on phones, you can find a micro-USB port, to which the corresponding headphones can be connected either directly (not all models) or through an appropriate adapter.
Features
- Unlike conventional headphones, the sound emitted by a USB connector is more powerful and clearer, thanks to the built-in amplifier. Some phone models and players have an additional amplifier, but very rarely, and the standard is not enough for some users.
- Some USB headphones that can connect via USB jacks do not need an external digital-to-analog converter because the headphones have their own chip with similar functionality.
Of course, there is a drawback to USB headphones: they are very power-hungry. Through the port flows a current of about 5 volts – the standard battery because of this can be discharged quite quickly. Of course, such a problem does not arise when you connect the headset to a computer or other fixed equipment.
Headphones with USB headphone jack

USB Type-C
After replacing the 3.5mm headphone jack, Apple started using USB Type-C in all its phones. Nowadays mini-jacks on the iPhone 7 and newer models are replaced with Type-C jacks. In addition, Micro-USB Type-C has greatly improved sound quality.
The pinout of the USB Type-C jack looks like this:
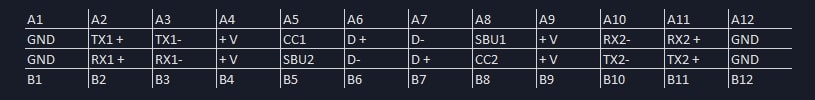

About the TRSS connector picture and its description in the article:
There are two wiring standards, with the picture showing the CTIA standard of Left/Right/Ground/Microphone. The text, however, mentions Left/Right/Microphone/Ground, which is the OMTP standard. While both are correct, this can be somewhat confusing without explanation. 🙂
Indeed, I edit that section to make it clearer and less confusing. Thank you for pointing it out!
thank you
Thanks for this, Very helpful.
This great info.
I get confused with the pictures and the text decriptions
best to put desription title above the picture