Can headphones cause tinnitus? A staggering 25 million Americans suffer from tinnitus, according to the American Tinnitus Association. This debilitating condition can lead to sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating, and emotional distress, and using headphones might be one major culprit.
This article will explore the connection between headphone use and tinnitus, discuss the signs of headphone-related tinnitus, and provide tips for protecting your ears from tinnitus.
A Brief Introduction to Tinnitus

This section briefly overviews Tinnitus, including its definition, symptoms, causes, and classifications, for those unfamiliar with the condition.
Definition and Symptoms of Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition that affects a person’s hearing and ear health, often manifesting as a persistent or intermittent phantom sound heard in the absence of ambient sound due to missing auditory nerves.
The most common Tinnitus symptoms are high-pitched ringing, buzzing, humming, or static noise-like noise. However, other symptoms include:
- Difficulty understanding speech in noisy environments
- Buzzing or hissing sounds in the ears
- Temporary hearing loss or muffled hearing after headphone use
- Persistent ringing or buzzing causing sleep disturbances
These distressing symptoms people with Tinnitus suffer may worsen while wearing headphones or after being exposed to loud environments.
Although not a serious health problem, tinnitus is often a symptom of other health issues, such as hearing loss or head trauma.
Causes of tinnitus
Causes of tinnitus range from earwax blockage to medication side effects. Henry et al. (2005) discovered that:
- A substantial 22% of cases were linked to noise exposure
- 17% were connected to head and neck injuries
- 10% to infections or neck illnesses
- 13% to medications or medical conditions
- The remaining patients could not identify a cause.

| Cause of Tinnitus | Description |
|---|---|
| Exposure to loud noise | Prolonged exposure to loud noise, such as attending concerts, using power tools, or listening to loud music, can damage the hair cells in the inner ear, leading to tinnitus. |
| Age-related hearing loss | As people age, their hearing ability tends to decline, which can result in tinnitus. |
| Earwax blockage | Excessive earwax can block the ear canal, causing hearing loss and tinnitus. |
| Ear infections | Infections in the middle or inner ear can cause inflammation, fluid buildup, and tinnitus. |
| Otosclerosis | This hereditary condition causes abnormal bone growth in the middle ear, leading to hearing loss and tinnitus. |
| Meniere’s disease | This inner ear disorder causes vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. |
| Eustachian tube dysfunction | The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, and when it doesn’t function properly, it can cause pressure changes in the ear and tinnitus. |
| Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders | Problems with the jaw joint can cause tinnitus, as the joint is located close to the ear. |
| Head or neck injuries | Trauma to the head or neck can affect the nerves, blood vessels, or muscles surrounding the ear, leading to tinnitus. |
Types of Tinnitus
There are three types of Tinnitus, each with its characteristics, causes, and manifestations.
- Subjective Tinnitus: The most prevalent type, accounting for over 99% of cases, characterized by an inaudible ringing, buzzing, or hissing noise only perceptible to the individual—regardless of volume.
- Objective Tinnitus: A rarer variant stemming from mechanical issues—such as elevated blood pressure or muscle contractions—near the ears.
- Pulsatile Tinnitus: Involving a rhythmic sound, this form correlates with nearby blood vessels and one’s heartbeat. Potential causes include vascular tumors, atherosclerosis, or idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
The downside of using headphones is that they can cause subjective tinnitus development due to prolonged exposure to loud music, damaging inner ear hair cells, which lose sensitivity or become irreparable, triggering the central gain control mechanism to compensate for the lost inputs.
Can Headphones Cause Tinnitus or Make it Worse?
It is crucial to recognize that noise trauma or loud music and tinnitus are closely linked, and the answer to “Can headphones cause tinnitus?” is a resounding yes.
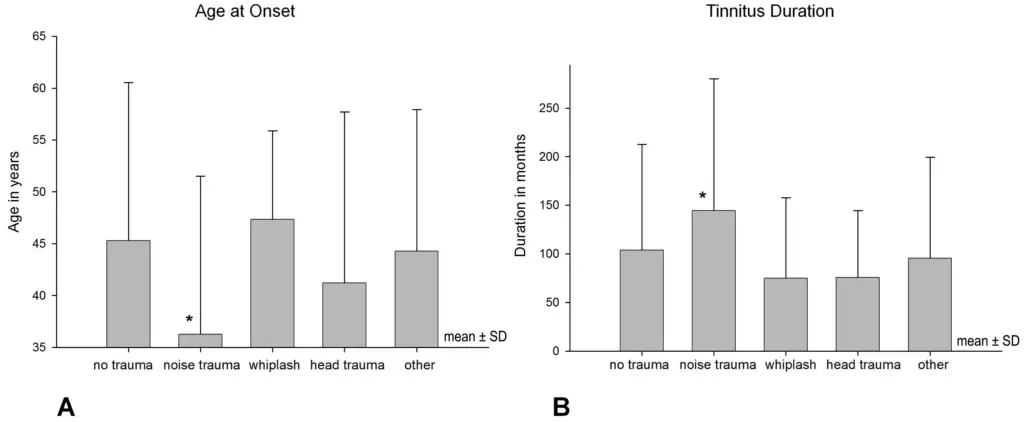
Fig.1 Illustrates that noise-induced tinnitus occurs earlier and lasts longer, posing a higher risk for the younger generation due to their exposure to loud environments like concerts, clubs, and personal audio devices.
The fact that 92.2% of individuals aged 13-18 utilize headphones, with over 70% listening for over an hour per day, further supports the argument that headphones can cause Tinnitus.
To prevent headphone-induced tinnitus, limit exposure to loud sounds by keeping volume levels within safe decibels (below 85 dB). Listening to music at high volumes for too long can cause permanent hearing damage and ear ringing. The risks of headphones on ears can be minimized by simply reducing the volume and duration of listening sessions.
How Headphones Can Induce Tinnitus and Hearing Loss
Noise exposure accounts for 22% of tinnitus cases, suggesting prolonged loud headphone use as a contributing factor. However, the relationship between headphone usage, Tinnitus and other hearing impairments is complex. It depends on factors like:
- Duration
- Sound intensity
- Headphone sound signature
- Headphone type
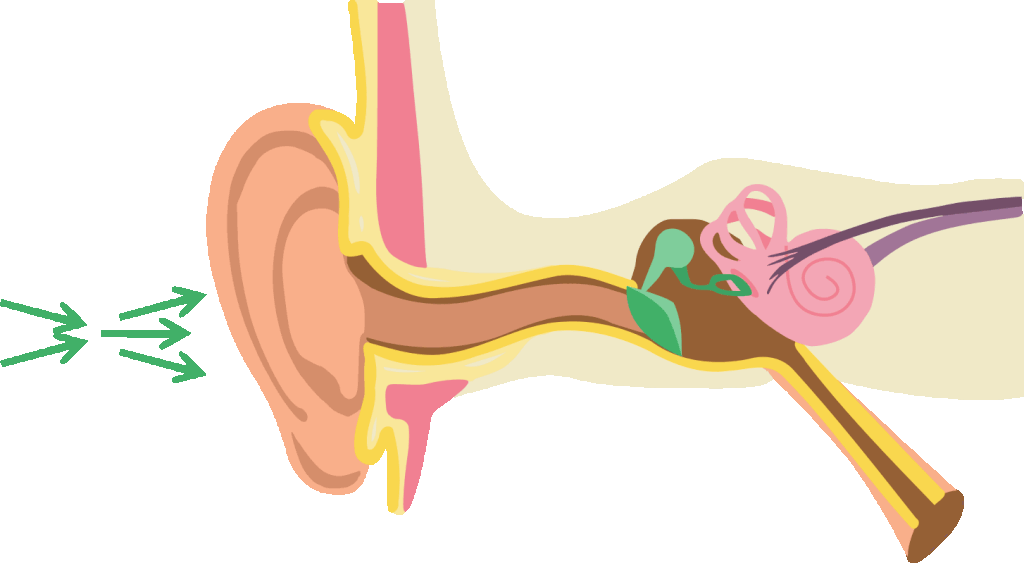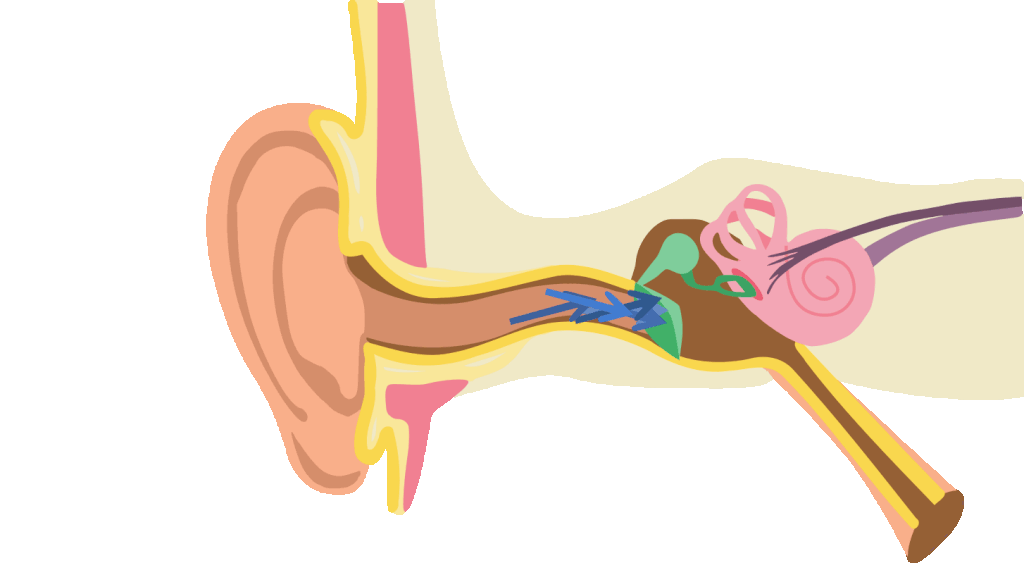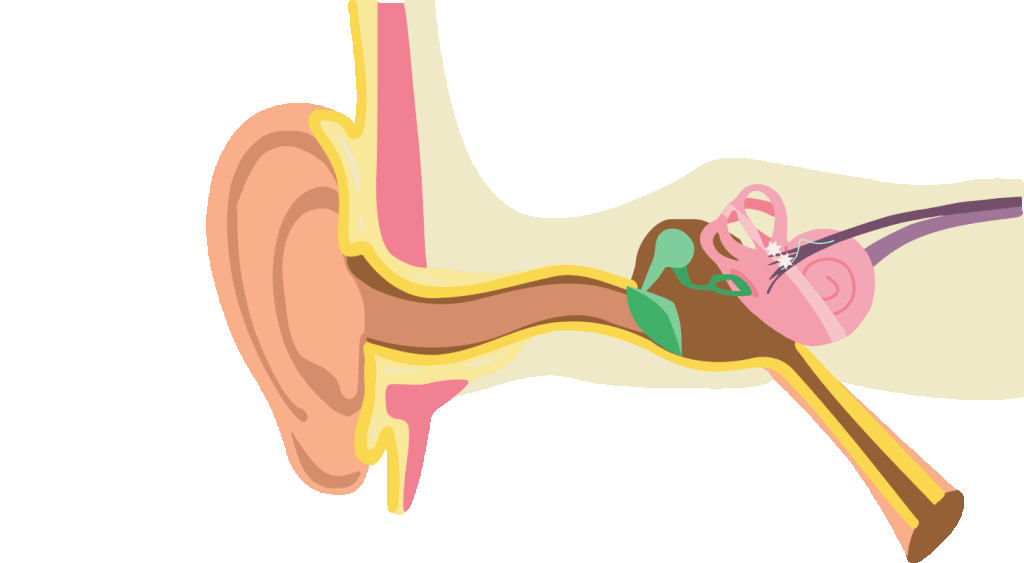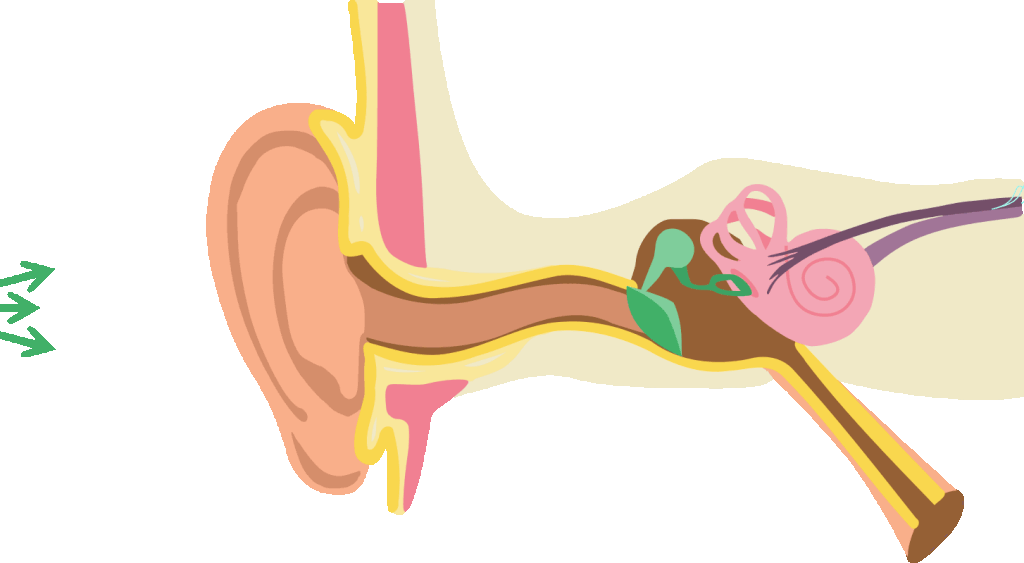
There are multiple ways headphones can harm ears; however, the severity of hearing loss and tinnitus caused by headphones is influenced by these factors, an age correlation and individual susceptibility to hearing damage.
When all variables are maximized, it’s like adding fuel to the fire, worsening the situation and increasing the risk of permanent hearing damage.
Damaged hearing receptors from exposure to high-frequency, high-pitched sounds lead to tinnitus, and loud music can even damage headphones themselves. So the main takeaway is to be aware of these risks and take necessary precautions to prevent worsening tinnitus or hearing loss.
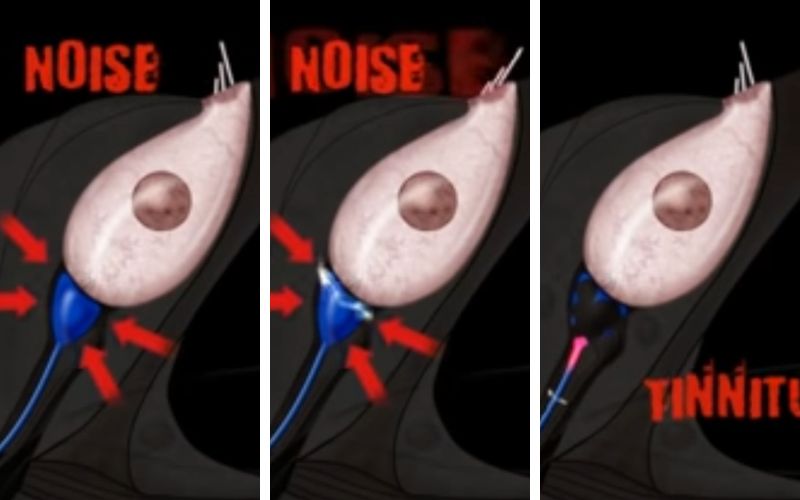
If the cause of Tinnitus is noise-induced, the cochlear hair cells are broken, that triggers an electrical impulse to the auditory nerve, without an external sound stimulus, which the brain interprets as sound.
The Psychological Impact of Tinnitus
There is a link between earphone use, tinnitus, and mental health. The role of headphones in causing tinnitus is primarily due to prolonged exposure to loud sounds, especially with in-ear headphones and earbuds, which can lead to noise-induced hearing loss.

With the help of MRI scans, audiometric tests, cognitive assessments, and self-report questionnaires, Tinnitus has been found to be linked with symptoms such as stress, anxiety, irritability, and depression.
Noise pollution can interfere with daily activities, disrupt sleep, and reduce overall quality of life, increasing stress and anxiety levels. However, constantly ringing in the ears only makes these problems worse, creating a feedback loop.
As a result, anxiety and depression are common in tinnitus sufferers due to the emotional impact of the condition. Tinnitus and stress form a vicious cycle, as stress exacerbates tinnitus symptoms.
Managing stress and practicing relaxation techniques can help alleviate tinnitus symptoms and improve overall mental well-being. Scheduling listening breaks and being aware of signs of listening fatigue can help prevent hearing damage.
Can Earbuds Cause Tinnitus?
The role of earbuds in tinnitus is a critical concern, as these compact audio devices can inadvertently contribute to this debilitating auditory disorder.

Earbuds, when used for prolonged periods, pose significant risks:
- Exacerbation of existing tinnitus: Prolonged exposure to loud volumes may worsen pre-existing tinnitus symptoms.
- Increased risk of developing tinnitus: If you’re free from tinnitus, constantly blasting music through earbuds may be “playing with fire,” which raises the risk of developing it.
- Temporary threshold shift: Listening to loud music through earbuds can cause a temporary decrease in hearing sensitivity, which may lead to tinnitus.
- Noise-induced hearing loss: Earbuds deliver sound directly into the ear canal, potentially causing damage to delicate hair cells.
So, do headphones or earbuds cause Tinnitus, or does prolonged exposure to loud noises lead to this condition?
As the saying goes, “It’s not the whistle that pulls the train.” In essence, headphones aren’t inherently dangerous; the risk lies in prolonged exposure to excessively loud music.
Because in-ear headphones are closer to the eardrum and delicate auditory sensors, one could say that over-ear headphones are safer than in-ear. The possibility of earbuds and IEMs causing Tinnitus and ear infections is also increased.
Additionally, multiple other harms can result from headphones. But why headphones hurt your ear often boils down to improper fit or misuse. So, don’t throw caution to the wind; use them responsibly.
Active Noise Cancelling Headphones and Tinnitus
Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) headphones can be a boon for individuals who want to avoid Tinnitus and noise-induced hearing loss (NIHS) by:
- Reducing external noise, enabling lower listening volumes.
- Providing a quiet environment, reducing stress—a common tinnitus trigger.
However, potential drawbacks include:
- Overuse potentially exacerbates tinnitus symptoms from a false sense of protection.
- Inadequate masking of high-frequency tinnitus, as ANC is more effective at attenuating low-frequency sounds but may produce residual high-frequency sounds, potentially irritating those with tinnitus.
To ensure ANC headphones don’t worsen your Tinnitus, buy only the most effective active noise canceling headphones, such as Bose QuietComfort 35 II, Apple AirPods Max, Sony WH-1000XM4, or B&W PX7. These headphones have been praised for their excellent noise-canceling capabilities in the high-frequency range and don’t produce extra residual noise.
They also won’t reduce the ringing in the ears. Noise-canceling headphones won’t worsen tinnitus in that the symptoms worsen. Still, according to Central Gain Theory, the absence of sound and lack of sound input from damaged hair cells may amplify internal noises, making tinnitus more perceptible.
Best Headphones for Tinnitus Sufferers
Protecting our ears and minimizing Tinnitus risk is crucial. Active Noise Cancelling (ANC) headphones with a warm sound signature and excellent noise reduction are highly recommended. A warm sound signature, reminiscent of a vintage tube amplifier, is gentle and soothing for Tinnitus sufferers.

For those already experiencing Tinnitus, open-back models are preferred as they don’t trigger symptoms like closed-back or noise-canceling headphones.
Consider these open-back headphones:
- Sennheiser HD 599: Comfortable, balanced, and suitable for extended listening.
- Grado SR80e: Lightweight, detailed sound, and wide soundstage.
- Philips SHP9500: Affordable, comfortable, and adjustable with EQ for Tinnitus relief.
If ANC technology is required, these headphones are the cream of the crop:
- Bose QuietComfort 45: Top-notch noise cancellation, comfortable
- Sony WH-1000XM4: Excellent noise cancellation, customizable sound, and adaptive sound control.
- Apple AirPods Max: Most consistent noise cancellation, elegant craftsmanship, and spatial audio feature.
Finally, check this article to see the headphones with the best passive noise reduction
Tips for Reducing the Risk of Tinnitus

Additionally, you can follow these steps to reduce your risk and protect your ears:
- Follow the 60/60 rule: listen to music at no more than 60% of the maximum volume for no more than 60 minutes.
- Choose over-ear headphones instead of earbuds, which produce lower sound pressure levels.
- Invest in noise-canceling headphones, which can help you listen to music at lower volumes by reducing background noise.
- Take regular breaks from headphone use to give your ears a chance to recover.
- Better prevent than cure: avoid exposure to loud noises, such as concerts, construction sites, or loud machinery, whenever possible. Also, use wear earplugs or earmuffs to protect your ears (they’re not cool, I know! but treat your ears right).
Conclusion
While headphones can potentially cause tinnitus, the risk can be minimized by following safe listening practices and choosing the right headphones. By being mindful of the volume and duration of your headphones, you can continue to enjoy your favorite tunes without risking your hearing.
