Are you among the users who have experienced the pain of hearing distorted sound from their computer but perfect crisp audio from their smartphone?
If so, you’ve probably wondered why your headphones sound so different when plugged into your computer.
The root cause behind your headphones sounding different on PC could stem from a variety of sources:
- Poor or loose connection between the headphone and computer
- An inferior PC sound card or audio source
- Improper audio settings or outdated audio drivers
- External interference in the form of an electromagnetic field near your PC or ground loop noise — causing the audio to become distorted, static, or muffled.
If you are experiencing problems with your headphone’s audio quality on your computer, don’t fear! In this article, we will analyze some of the common causes why your headphones may sound different on PC and provide you with valuable tips on how to fix and troubleshoot the problem.
So read on to find out more!
Reasons Why Headphones Sound Different on PC
We can identify various explanations for why headphones sound different on PC, each having a different effect on the audio output. We list here some of the most common causes below:
- Integrated sound card of PC or laptop is of inferior quality—leading to lackluster output.
- Out-of-date or corrupted audio drivers
- Static or electrical noise from EMI, ground loop noise, or poor connection.
- Different or wrongly configured EQ settings in the system.
Low-Quality Onboard Sound Card
Different sound quality when using headphones on a PC is likely due to a sub-par built-in sound card with low-quality Realtek chips (i.e., AC97 or HD Audio).
Often, a faulty headphone jack can also be the culprit. The ground wire fails to make contact with the plug, causing the sound from the left and right channels to become unbalanced.
What’s more, some audio interfaces come with a 4-pin audio combo jack, allowing connections for microphone and headphone use, which is not ideal as it can bring about various issues like distortion and poor sound quality, and failure to separate the two audio channels properly.
Therefore, to ensure better sound output in your PC, it is best to buy an external sound card. This will also allow you to use additional features like:
- Bass and treble gain options
- Adjustable sound output using controls
- Digital and analog audio ports
Recommended External Sound Cards
- Sound BlasterX G6 Hi-Res
- Creative Sound Blaster X4 Hi-Res 24bit/192kHz
- FiiO E10K-TC External Sound Card
Out-Of-Date or Corrupted Audio Drivers
When outdated, corrupted, or faulty drivers are to blame, headphones can sound strange on a PC—or even flat-out refuse to produce sound. Even Microsoft’s Windows audio troubleshooting guide recommends keeping drivers up-to-date as the first step in solving audio issues!
To keep headphones at their best, regular driver updates are a must:
- Outdated or corrupted audio drivers can cause audio issues, like headphones not showing up, no sound output, the sound coming out distorted, and more
- Making sure your laptop/PC and software have compatible drivers can be accomplished by downloading them manually from the device manufacturer’s website
- Or by allowing Windows (or whichever OS you’re running) to keep them up-to-date automatically
Static Noise & Electromagnetic Interference
Headphones can sound notably different on a PC due to a range of issues, many of which are related to static noise, poor grounding, wireless interference, a dirty headphone jack, or connection to bad audio sources.
Static Noise
Hums and static noise is caused by Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) or poor grounding, producing an unbalanced and low-level buzzing sound in the background. To reduce ground noise, an audio isolation transformer or DAC (digital-to-analog converter) can be used effectively to buffer and cut out the low-level interference.
Using power surge protection, disconnecting your laptop’s DC power supply when listening to music, and increasing the maximum processor state can be helpful.
Wireless Interference
Wireless interference can occur from various electromagnetic sources such as WiFi networks, microwaves, and fluorescent lights. The 2.4 GHz frequency range can get disrupted, resulting in a distorted connection and poorer sound quality. Objects such as glass, metal, concrete, and even water can block or absorb the signals between your Bluetooth headset and PC.
To reduce wireless interference, Bluetooth headphones should be used in an area with minimal environmental distractions and factors that can block the signal.
Dirty Headphone Jack
Dirty headphone jacks (the bane of many music lovers) can sometimes lead to static buzzing noises. If this occurs, clean the headphone jack with isopropyl alcohol and a q-tip. Also, plug the headphones in and out of the port and wriggle it around. This can help remove any oxidation layer and create better contact between the jack and port.
Different System-Wide Audio Equalizer Settings
System-wide audio equalizer settings significantly impact sound output when using headphones. This includes the settings in the operating system, media player software, or headphone audio processor.
Depending on the settings chosen, different EQ presets on different devices can drastically alter the sound quality and music playback. Apps such as Equalizer APO can also modify the sound output on a PC. And, if unaware, you’re probably using different EQ presets on other devices, which creates a difference in sound between the different devices.
So far, all these factors can significantly alter the way your headphones sound and create noticeable differences in audio quality.
Note: Some Bluetooth headphones, like Sony WH-1000XM3, can store in their DSP different EQ settings within the application depending on the device it is paired with. The EQ settings don't carry over to your PC or other devices.
Windows 10 Equalizers
These Windows 10 compatible EQs may be the culprit for hearing your music differently on a PC. To troubleshoot why headphones sound different on PC, disable them or adjust the EQ to match the settings on other devices.
How to Improve Headphones Sound on PC
Headphones can sound incomparable on a PC due to a variety of reasons. Fortunately, there are numerous techniques to make headphones sound better on PCs:
- Run the Audio Troubleshooter
- Update audio drivers
- Use the sound card audio port (the one in the back of your PC)
- Disable Audio Enhancements to reduce any potential sources of sound distortion
- Increase the system Power Options to reduce hissing noises on laptops
Troubleshooting Windows Audio
When attempting to improve the sound quality of your headphones on PC, users should first take advantage of Window 10’s built-in troubleshooting tool, a handy tool that can help diagnose and fix sound-related issues.
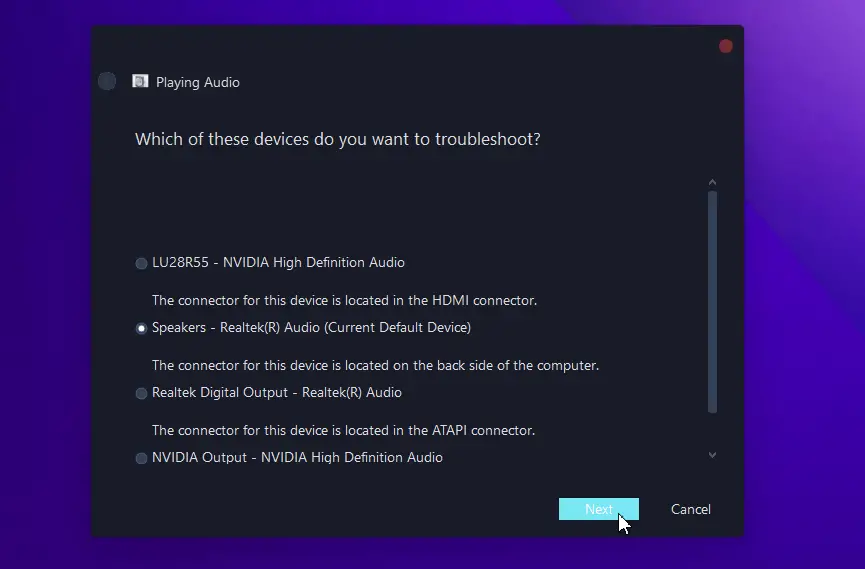
To use the Windows Audio Troubleshooter:
- Launch the Settings program using the
Windows + Ikey combination. - Open the System tab and go to the Sound section.
- Click on the Troubleshoot button to troubleshoot sound system.
- Select the audio device from the displayed list and press Next.
- Follow any proposed instructions to repair any audio issues detected.
A much easier way to run an audio troubleshoot is to right-clicking on the Speaker icon located in the system tray and choose the Troubleshoot sound problems option.
Often, performing a scan with Windows Audio Troubleshooter will fix the bad sound quality in your headphones by itself.
Update Audio Drivers
In the event the audio troubleshooter couldn’t fix issues related to outdated or corrupted drivers, manually updating the audio drivers requires a few simple steps:
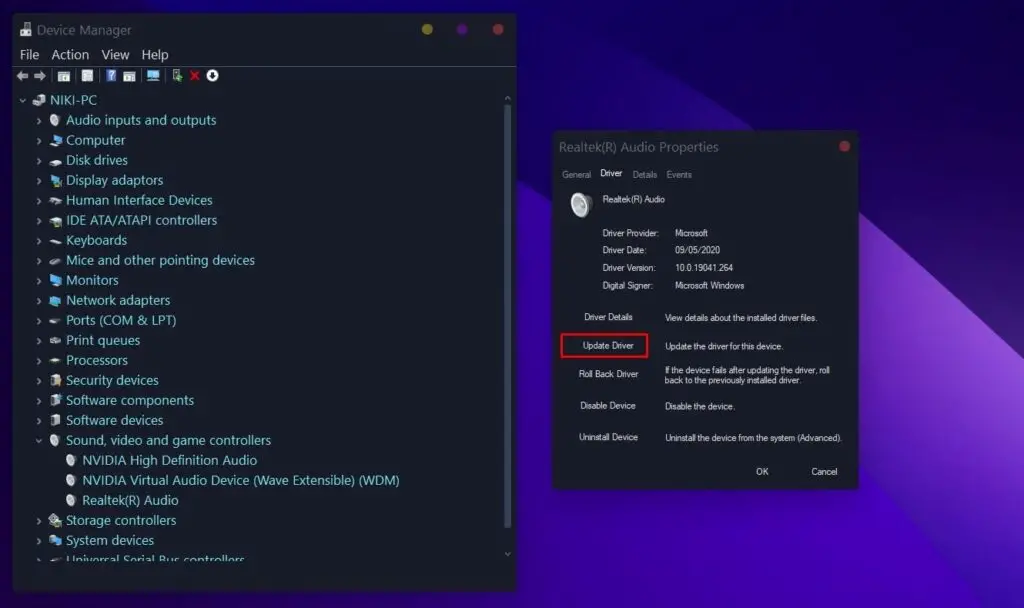
- Open the Device Manager.
- Expand the “Sound, video, and game controllers” section.
- Right-click on “Realtek(R) Audio” and select “Update Driver”.
- Select “Search automatically for updated driver software”.
- Finish up any on-screen instructions and complete the installation process.
- Restart your computer.
If you have to reinstalling your audio drivers from your personal computer, navigate to Device Manager and uninstall them from “Sound, video, and game controllers” and “Audio inputs and outputs”. Windows will install them back after you restart your PC.
It is also a good idea to install drivers provided by the headset’s manufacturer (or sound card’s). A device detection utility such as DriverFinder can help in this regard.
Use The Sound Card Audio Port
Many committedly avoid utilizing the audio port from the front panel, which connects to the motherboard, as this can adversely diminish audio quality, and also causes static when volume is increased due to the electrical interference of other components.

Are Sound Cards Worth It?
For improved sound quality and to get rid of residual interference, it is best to plug headphones into the soundcard’s audio port—an option that should be always considered by those seeking to maximize their auditory experience.
Furthermore, a sound card is well worth using because it has the following advantages:
- Eliminates static and interference from other components
- Improves sound quality through higher bit-rate and sample rate
- They’re isolated from noisy components and power issues
- Can provide support for 5.1 & 7.1 surround sound
Disable Audio Enhancements
If all else fails, try disabling audio enhancements. Other features like Windows Sonic for Headphones and Dolby Atmos for Headphones can change how your headphones sound on PC and generate annoying static noises at high volume levels.
To disable Audio Enhancements:
- Launch the Settings program using the
Windows + Ikey combination. - Open the System tab and go to the Sound section.
- Click on the Device Properties button.
- Within this window, locate the Enhancements tab and make sure no options are checked.
- Press Save and exit out of the window.
Disable all sound effects to ensure your PC has the same listening conditions as your other device before making drastic changes like purchasing a DAC/Amp.
Adjust Power Options
Laptop users must increase the Power Options to prevent any power-saving features from causing interference, reducing the sound quality, or muffling the audio. This adjustment also solves the issue of headphones crackling and popping sounds when plugged into laptops.
To increase laptop’s Power Settings:
- Right-click on the Start button and select Power Options.

Navigate to Start Menu to open Power Options - Select “Additional power settings” from the left sidebar.
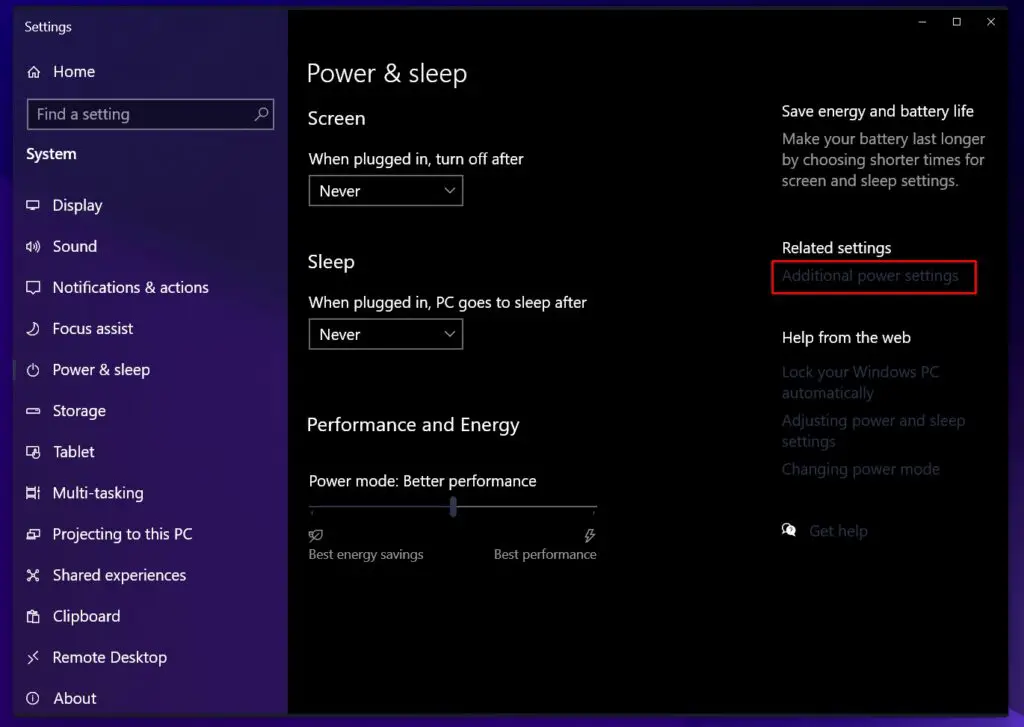
Select Additional Power Settings - Choose your plan, for example, Balanced mode, then click Change Plan Settings.
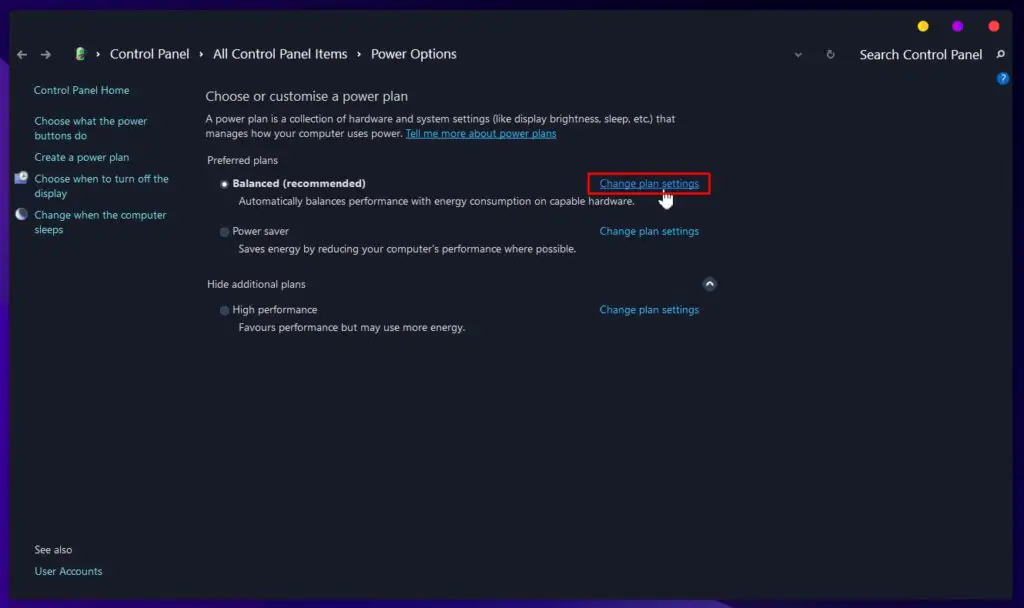
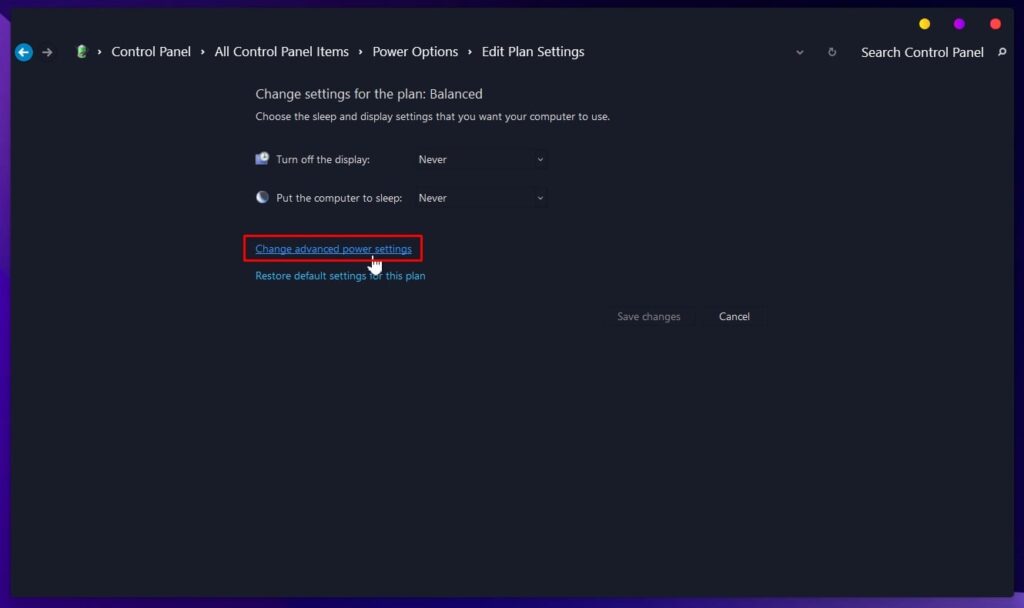
Select Preferred Power Plan and Change Plan Settings - Click on Change advanced power settings.
Change Advanced Power Settings - Under the Processor Power Management section, adjust the Min Processor state and Max Processor State to 100% for both On battery and Plugged in.
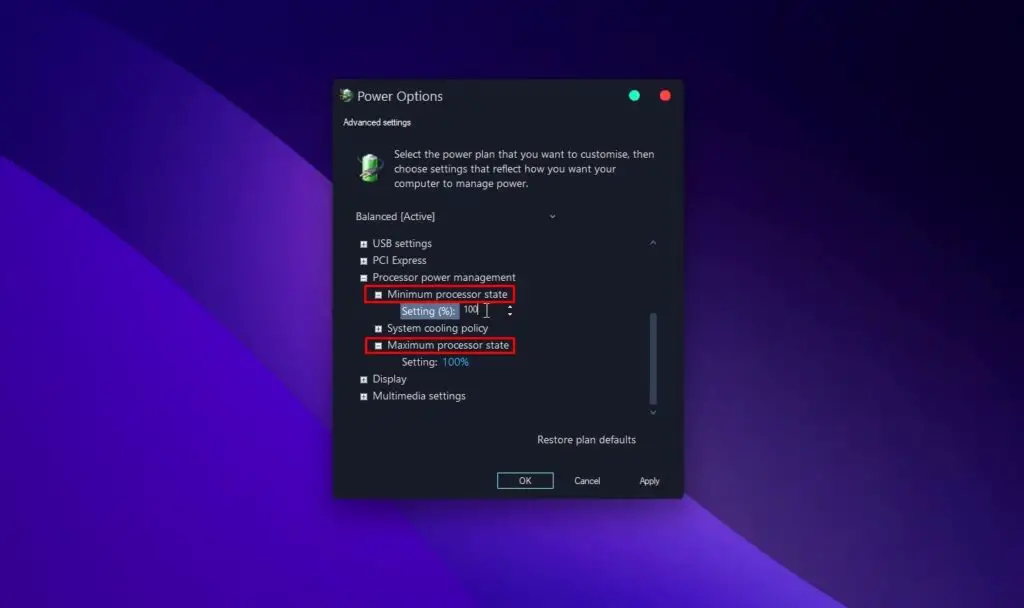
Set Min & Max Processor State to 100
Another handy practice is unplugging the laptop charger when the headphones are plugged in to reduce static and buzzing.
Ultimate Performance Power Plan
The Ultimate Performance Power Plan, although not available as a default feature on Windows 10 Home and Pro, along with laptops due to limited battery power resources, can be enabled to maximize PC performance.
To enable it, use Command Prompt:
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run command - Type
cmdand press Enter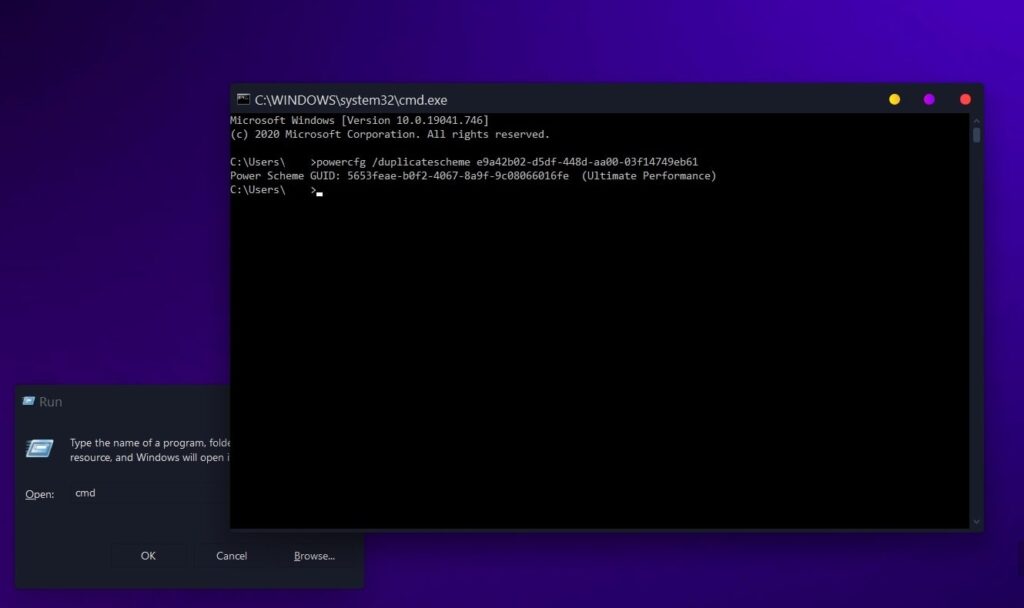
Open Run Command, Type cmd and Paste The Code - Type
powercfg /duplicatescheme e9a42b02-d5df-448d-aa00-03f14749eb61and Enter to enable the Ultimate Performance Power Plan.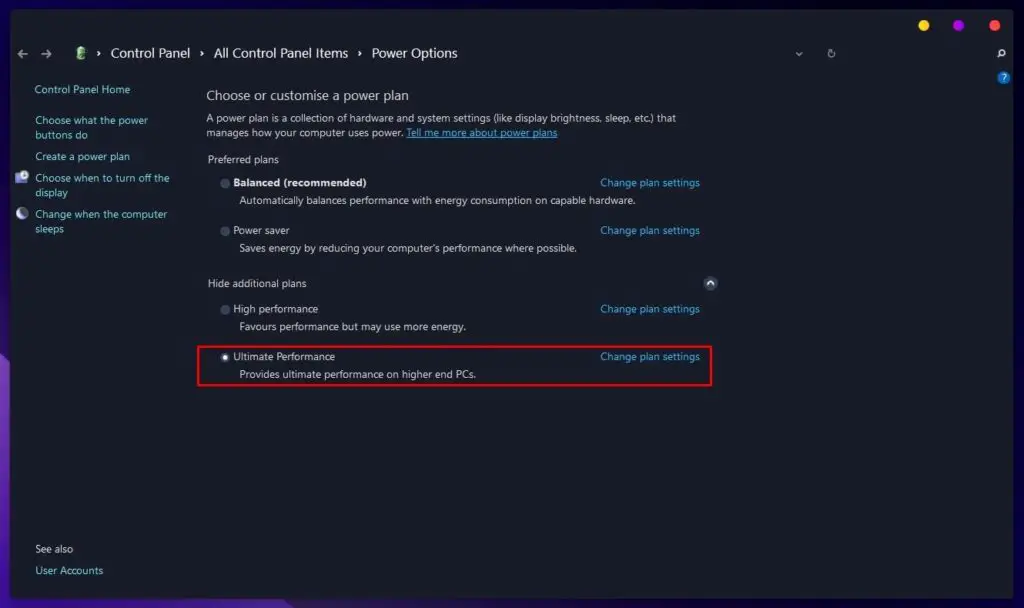
Use Ultimate Performance plan (if necessary)
Difference Between Ultimate Performance and High Performance
- High performance mode runs the CPU at its maximum P-state, but does not affect C-states.
- C-states (such as C6 and deeper states, plus package C-states) create latency, mainly due to power savings by way of clock/voltage gating at idle.
When enabling Ultimate Performance Power Plan, all C-states will be “dropped” and no longer present in the system, and the CPU will work at maximum speed constantly.
The reduced latency is important for music producers, which is why low-latency PC audio is vital. It’s also important for headphone users who experience static or buzzing noise when listening to music. This power plan uses a lot of power (something worth noting).
Ultimate Performance vs. Balanced (recommended)
In most cases, you should use the “Balanced plan.”
Balanced offers the best of both worlds: efficient power-saving when idle, snappy performance when under load.
Bluetooth Headphones Sound Bad on PC: Why It Happens And How to Fix It
Listening to music wirelessly can be convenient, but Bluetooth headphones sound can vary greatly when used on a PC (sometimes the sound is downright bad) due factors such as:
- Connecting them as a headset rather than stereo headphones.
- Inneficient data transmission: Codecs mismatch can result in sound distortion as a result of using low-end/inefficient codec.
- Bluetooth headphones placed near computer speakers and sources of electromagnetic radiation
Bluetooth Headphones Connected as Headsets
When connecting wireless earbuds or Bluetooth headsets to PC, the system offers two methods:
- Headphones: providing stereo audio
- Headset: delivering playback and hands-free communication
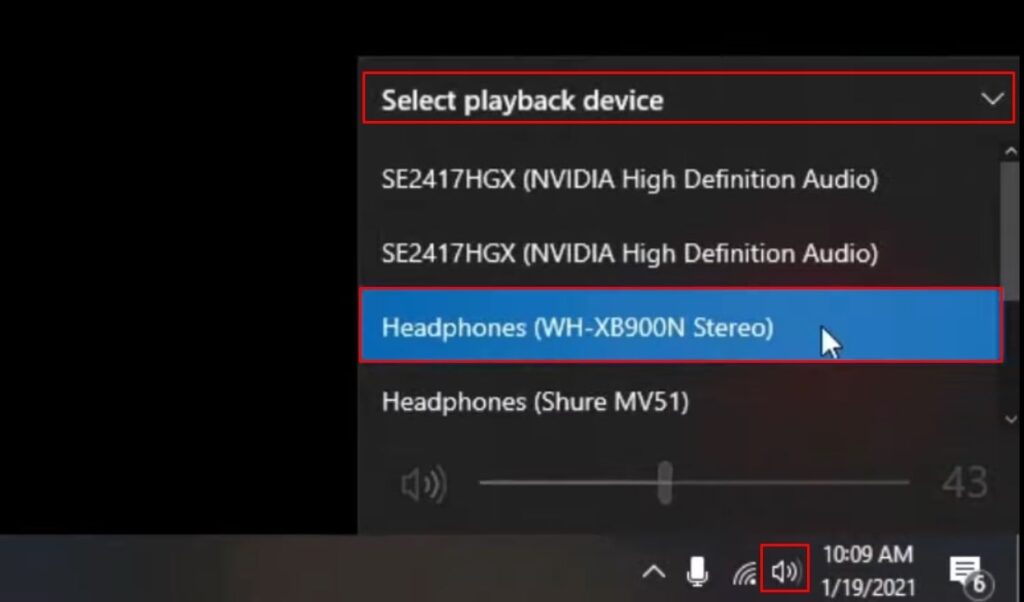
The Stereo mode is for playback of sound and music, for example, through browsers or media players like Spotify and Winamp.
The Headset option causes sound issues, such as distortion, buzzing noises, and increased latency, making your Bluetooth headsets sound awful on PC. This results from the additional channel used for microphone signals.
So, for the best sound quality, connect your Bluetooth headphones as Headphones, not Headsets.
Codec Mismatch & Low Data Transmission Rate
Codec-induced distortion is a consequence of audio compression algorithms employed with Bluetooth headphones, resulting in inferior sound quality. The limited data that can be transmitted depends on the Bluetooth codecs shared by both devices.
Experience shows that disappointment can likely be avoid if consumers do the necessary work and research, i.e., determining which codecs are included in the Bluetooth headphone’s specs and ensuring that the same codecs are supported by their favored audio source (e.g., smartphone, tablet, Mac, or PC). Otherwise, they may wind up with SBC audio compression.
To avoid low-quality audio via wireless, take these aspects into account:
- Look into headphones or Bluetooth digital-to-analog converter (DAC) with codecs like aptX, AAC, and LDAC
- Ensure that your Win 10/11 PC or Mac supports the same codecs.
Recommended High-Resolution Bluetooth DAC
- FiiO BTR5-2021 Headphone Amps Bluetooth 5.0 Receiver
- FiiO BTR3K Receiver Amplifier Bluetooth Headphone
- TOPPING G5 LDAC Portable Bluetooth DAC & AMP
Putting Bluetooth Headphones Near EMI Sources
When using Bluetooth headphones, one should be cautious of their proximity to sources of Electromagnetic Interference (EMI), including computer speakers, unwanted radio waves and other devices that communicate via 2.4 Ghz frequencies.

Similar to how EMI affects visuals in television/radio signals, it can also have an effect on audio.
The wireless signal interference creates audio skipping and distortion, which can be caused by magnetic field radiation nearby. In environments with a high EM radiation level, the noise level can be more pronounced.
Ideally, the headphone should be placed away from any EMI sources (not face towards them) to avert sound skipping and/or distortions due to the switching frequency mainly made up of harmonics of the 2.4GHz band that is generated internally by the Bluetooth headphone’s battery.
Furthermore, using them via cable connection for sound instead of Bluetooth can help avoid these audio issues.
Conclusion
In this article, we outlined some of the common causes for why your headphones might sound differently on your PC that includes poor connection between the headphone and computer, inferior sound card, improper audio settings or outdated audio drivers, and external interference.
With these useful tips, you should be able to identify and resolve sound discrepancies on your PC. Have you tried any of these strategies? Let us know in the comments! Share your experience in the comments below!
